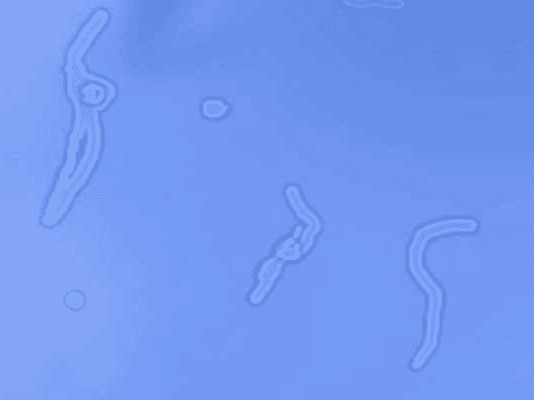
What Are Floaters?
Floaters are small spots, lines, or shapes that appear to drift across your field of vision. Many people describe them as gray or black specks, cobweb-like strands, or blurry shadows that move as your eyes move. Floaters are especially noticeable when looking at something bright, such as a clear sky or a blank wall.
Floaters are small clumps of cells or protein that form in the vitreous layer of your eye (the clear gel-like substance inside the eye that helps maintain its shape). As light enters the eye, it passes through the vitreous on its way to the retina. When these clumps of cells form, they cast tiny shadows on the retina, and that’s what you see as floaters.
Are Floaters Normal?
For most people, floaters are a normal, easpecially as you age. The vitreous inside the eye becomes more liquid as you get older, and this change can lead to the development of floaters. It’s common for people to notice floaters more frequently with age, and they’re usually harmless. Most floaters eventually settle at the bottom of the eye and become less noticeable over time.
While floaters are typically a natural part of aging, they can occasionally appear in younger people due to certain eye conditions or trauma. For example, individuals who are nearsighted, have undergone cataract surgery, or experienced eye injuries may notice floaters earlier in life.
Can Floaters Be a Sign of a Serious Problem?
In some cases, the sudden appearance of many floaters or an increase in floaters could indicate a more serious issue. One such condition is a retinal tear or retinal detachment, which can occur when the vitreous pulls away from the retina. This condition requires immediate medical attention to prevent permanent vision loss.
Other signs that might accompany floaters and signal a problem include flashes of light, loss of peripheral vision, or a shadow appearing over part of your vision. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see an eye doctor right away for an evaluation.
How Are Floaters Diagnosed?
If you notice new or worsening floaters, an eye doctor can perform a comprehensive eye exam to determine the cause. During the exam, the doctor will dilate your pupils to get a clear view of your retina and vitreous. This allows them to check for any signs of retinal tears, detachment, or other conditions that could be causing the floaters. In most cases, floaters are simply a part of the aging process and aren’t cause for concern.
Can Floaters Go Away on Their Own?
While floaters don’t disappear completely, they often become less noticeable over time. This is because the clumps or strands causing the floaters tend to settle in the vitreous, moving out of your line of sight. As your brain becomes accustomed to them, it also learns to ignore their presence, making them less distracting.
Should You Be Concerned About Floaters?
For most people, floaters are a normal part of life and nothing to worry about. They’re usually harmless and don’t interfere with vision in any significant way. However, if you notice a sudden increase in floaters, flashes of light, or any changes in your vision, it’s important to consult with an eye care professional to rule out more serious issues.
Discover independent eyewear with Project Spex. Every Friday, we deliver the latest in collectible eyewear and your favorite independent designers.
Sign up now and never miss a thing!
About The Author:

Will Benjamin is an advocate for independent eyewear and one of the driving forces behind Project Spex. With a passion for unique, collectible, and limited-edition eyewear, Will aims to inspire people to build their own collections through Project Spex, while supporting the success of independent opticals.